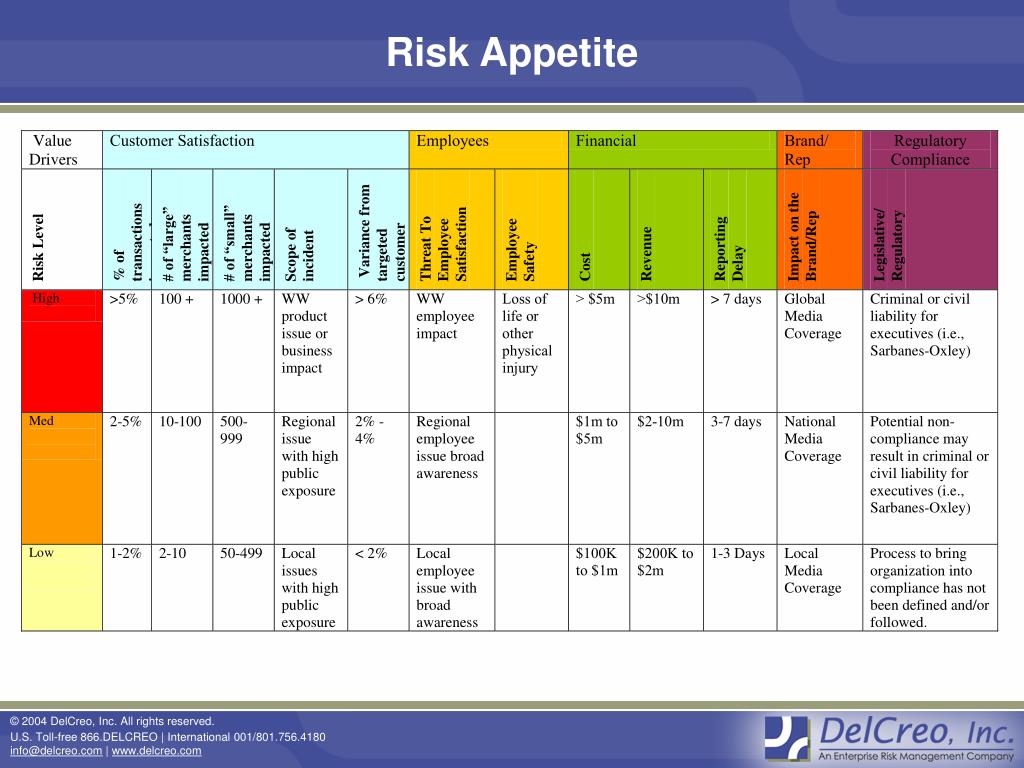
Explore the intricate world of risk appetite in finance, a crucial concept that guides individuals and organizations in making sound investment decisions. Understanding risk appetite involves evaluating one’s willingness to take risks in pursuit of financial goals, an essential element in the realm of finance. Assessing and setting a suitable risk appetite is vital to achieving a balance between risk and reward, ultimately influencing investment strategies and outcomes.
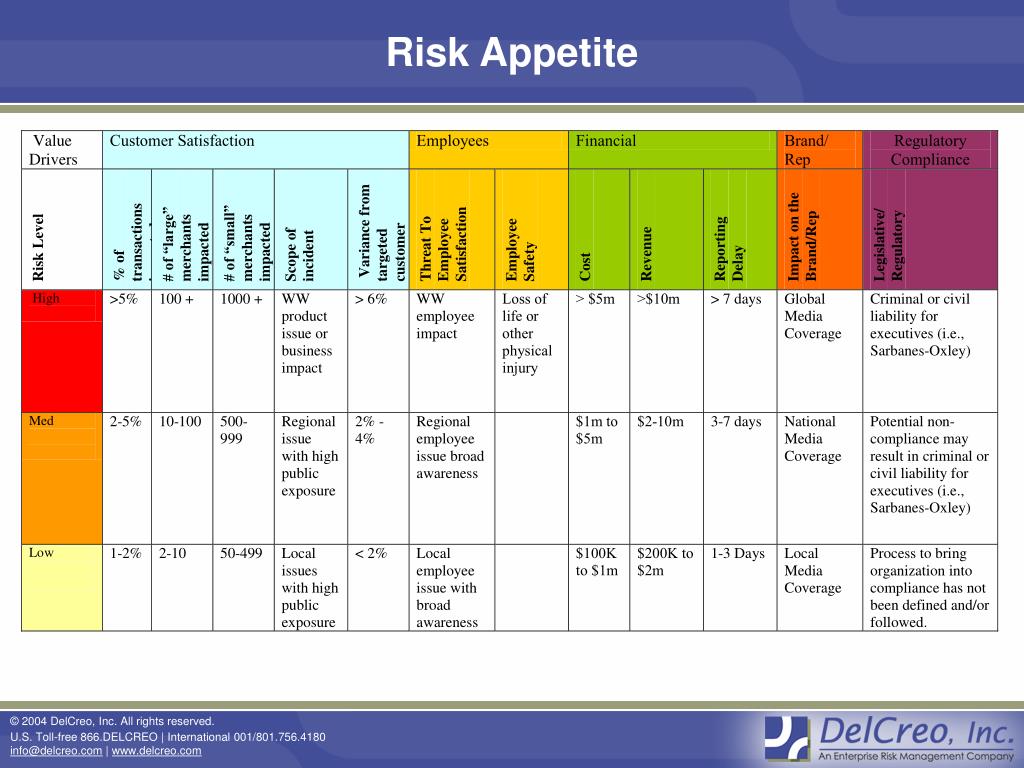
Unveiling the Essence of Understanding Risk Appetite in Finance
In the realm of finance, understanding risk appetite is paramount. It defines one’s willingness to endure risk for potential financial gains, crucial in decision-making processes. Key elements like risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment objectives shape one’s risk appetite profile, guiding strategic choices.
Factors influencing risk appetite are multifaceted, encompassing personal circumstances like financial stability, market conditions such as volatility, and regulatory mandates. Aligning these elements harmoniously is fundamental in crafting a robust risk management framework.

Setting an Appropriate Risk Appetite
Guidelines for Setting an Appropriate Risk Appetite
Setting a fitting risk appetite involves a meticulous evaluation of individual circumstances and financial objectives. Tailoring risk tolerance to align with personal goals ensures a balanced approach to risk management. Understanding one’s capacity to withstand fluctuations in investment performance is key in striking the right balance between risk and return.
Strategies for Aligning Risk Appetite with Investment Portfolio and Financial Plan
Harmonizing risk appetite with investment portfolios and financial plans demands a strategic approach. Diversification plays a vital role in mitigating risks associated with investments. Allocating assets across various asset classes can help spread risk and optimize returns, aligning with the identified risk tolerance levels.
Importance of Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting Risk Appetite
Regularly reviewing and adjusting risk appetite is crucial to adapt to changing circumstances. As financial goals evolve or market conditions fluctuate, reassessing risk tolerance ensures that investment strategies remain in line with the desired outcomes. Flexibility in adjusting risk appetite enables a proactive response to dynamic financial environments.
In summary, setting an appropriate risk appetite involves customizing risk tolerance based on individual circumstances and financial objectives. By strategically aligning risk appetite with investment portfolios and regularly reviewing and adjusting it as needed, individuals can navigate the intricate world of finance with confidence and optimize investment outcomes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DeterminingRiskandtheRiskPyramid3-1cc4e411548c431aa97ac24bea046770.png)
Risk Appetite and Investment Decisions
Understanding the Impact of Risk Appetite on Investment Decisions
Risk appetite plays a fundamental role in shaping investment decisions, impacting crucial aspects like asset allocation and diversification. Investors with a high-risk appetite may opt for more aggressive investment options to seek higher returns, while those with a conservative risk stance would lean towards safer, lower-risk investments.
Tailoring Investment Strategies to Different Risk Appetites
Tailoring investment strategies to align with different risk appetites is essential for optimizing financial outcomes. Conservative investors often favor stable assets like bonds, focusing on capital preservation. In contrast, aggressive investors may pursue growth stocks or venture into riskier markets to potentially achieve higher profits, but at the expense of increased volatility.
Achieving Financial Goals through Aligned Investment Decisions
Aligning investment decisions with one’s risk appetite is paramount in achieving financial objectives. A mismatch between risk tolerance and investment choices can lead to suboptimal results, jeopardizing the attainment of long-term financial goals. It is crucial to strike a balance between risk and return, tailoring investments to reflect one’s risk appetite for a more successful investment journey.
By elaborating on the intricacies of risk appetite’s influence on investment decisions, providing insights into various investment strategies corresponding to different risk profiles, and emphasizing the importance of aligning investment choices with risk preferences to meet financial goals, individuals and organizations can navigate the complex financial landscape with clarity and purpose.
The Role of Risk Appetite in Financial Planning
Risk Appetite in Financial Planning
Understanding Risk Appetite in Finance is integral to financial planning. It dictates the level of risk an individual is willing to take to achieve their financial objectives, influencing investment choices in retirement and estate planning scenarios.
Strategies for Managing Risk
Managing risk in financial plans involves diverse strategies like insurance coverage and creating emergency funds, aligning risk tolerance with long-term financial goals for a balanced approach.
Tax Implications in Risk Management
Considering tax implications is crucial in risk management within financial plans. Strategic tax planning can optimize returns and minimize liabilities, enhancing overall financial stability and growth.
The Influence of Behavioral Biases on Risk Appetite
Behavioral Biases’ Impact on Risk Appetite
Behavioral biases significantly affect risk appetite and investment choices. Biases like overconfidence may lead individuals to take excessive risks, while loss aversion can make them overly cautious. Understanding these biases is crucial for aligning risk appetite with financial goals.
Common Behavioral Biases in Finance
Two prevalent biases affecting risk appetite are overconfidence, where individuals overestimate their abilities, and loss aversion, which causes a stronger reaction to losses than gains. Recognizing and addressing these biases is essential for making sound financial decisions.
Mitigating Behavioral Biases in Risk Assessment
To combat the negative impact of biases on risk appetite, individuals can employ strategies like diversification, setting clear investment goals, and seeking advice from professionals. By acknowledging and addressing these biases, investors can make more rational and balanced risk decisions.