Are you interested in delving into the world of qualitative analysis methods? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of qualitative analysis, data collection techniques, and the advantages they offer to researchers. Understanding the nuances of qualitative analysis is crucial for conducting in-depth research and gaining valuable insights into the subject matter. Dive into the realm of qualitative analysis and uncover its significance in the realm of research.

Understanding Qualitative Analysis: A Comprehensive Overview
Qualitative analysis, a cornerstone of in-depth research, delves into the subjective realm of human experiences and viewpoints. Unlike quantitative methods, it focuses on non-numerical data sources like interviews, observations, and textual materials. Researchers engaging in qualitative analysis aim to unravel profound insights into the studied subject matter and the unique perspectives of the participants involved. This method finds its prime application in disciplines like sociology, anthropology, and psychology, enriching research with contextual depth and nuanced understanding.

Exploring Different Types of Qualitative Analysis Methods
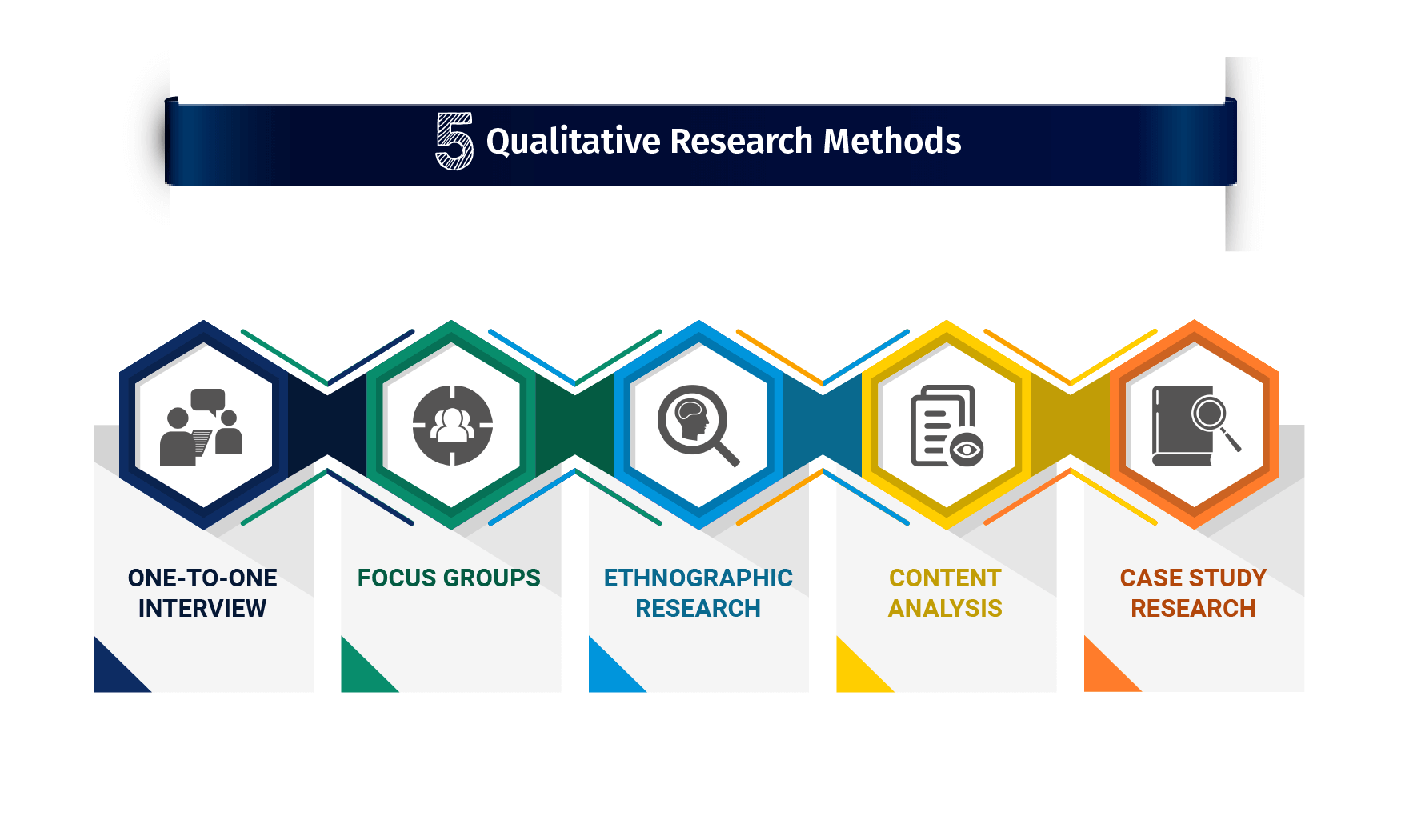
Qualitative analysis methods encompass a diverse range of approaches, each bringing unique strengths and weaknesses to the research process. Among the commonly employed methods are grounded theory, focusing on theory development; phenomenology, aimed at exploring lived experiences; ethnography, delving into cultural contexts; and case study, offering in-depth examinations of specific cases. The selection of a method hinges on factors like research inquiries, data characteristics, and theoretical frameworks, guiding researchers towards distinct data collection, analysis, and interpretation pathways.

Exploring Data Collection Techniques in Qualitative Analysis
In the realm of Qualitative Analysis Methods, data collection is a multifaceted process comprising in-depth interviews, observations, and document analysis. Interviews stand out as a cornerstone, offering a platform for researchers to extract detailed and profound insights from study participants. These interactions pave the way for a deeper understanding of the research subject, enriched by the nuances of human expression and experience.
Observations in qualitative analysis methods provide a unique vantage point into the natural settings where behaviors and interactions unfold. By immersing themselves in the context under study, researchers can capture the subtleties and intricacies that may go unnoticed in more structured research approaches. Observations offer an unfiltered view of phenomena, enriching the depth of the analysis with real-world dynamics.
Document analysis, another essential facet of data collection, delves into the wealth of written materials that encapsulate the essence of the research landscape. By scrutinizing transcripts, diaries, emails, and other textual artifacts, researchers can unearth valuable insights, trends, and patterns. Document analysis complements interviews and observations, offering a textual dimension to the qualitative analysis process, enhancing the richness and comprehensiveness of the study.
Advantages of Using Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis offers a window into the intricate tapestry of human experiences and perspectives, delving deep into emotions, motivations, and context that quantitative data might overlook. By embracing narratives and context, researchers can uncover rich layers of meaning that shape human interactions and behaviors, providing a holistic view of the studied phenomena.
Exploring complex and multifaceted phenomena is a forte of qualitative analysis, enabling researchers to unravel intricate relationships, behaviors, and perspectives that quantitative methods might oversimplify. Researchers can navigate through the nuances and intricacies of human experiences, delving into subjective realities and uncovering the underlying frameworks that shape them.
The flexibility of qualitative analysis empowers researchers to craft tailored methodologies that fit the unique demands of their research inquiries. Whether using interviews, observations, or content analysis, researchers have the freedom to adapt their approaches, fostering a dynamic research process that can accommodate evolving research questions and emerging insights.
Delving into cultural, social, and psychological dimensions of human behavior is where qualitative analysis shines. By immersing in the lived experiences and social contexts of individuals, researchers can grasp the intricate interplay of culture, society, and psyche, shedding light on the underlying meanings, norms, and values that influence human actions and interactions.

Applications of Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis finds extensive applications across disciplines like sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education, shaping research methodologies and enhancing findings. By delving into social issues and cultural practices, researchers can unveil the intricacies of human behavior and societal dynamics, paving the way for deeper insights. Moreover, the utilization of qualitative analysis plays a pivotal role in informing policy decisions, aiding program development, and facilitating effective social interventions. The nuanced approach offered by qualitative analysis allows for a profound comprehension of multifaceted social phenomena, enabling researchers to address complex societal challenges with clarity and depth.
