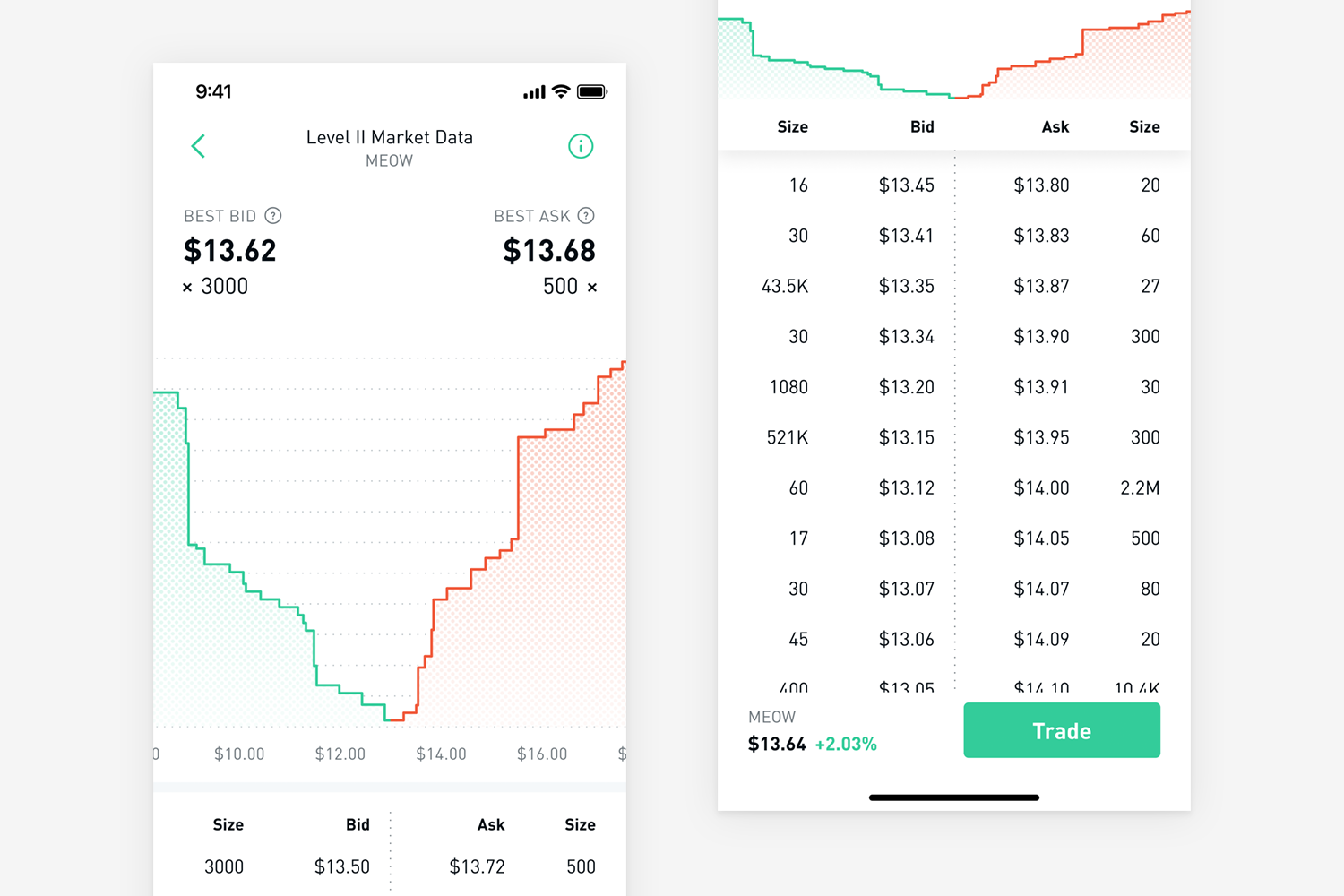
In the world of trading, understanding bid and ask prices is essential for making informed decisions. The bid price refers to the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a security, while the ask price is the minimum price at which a seller is willing to sell. These prices play a crucial role in determining the entry and exit points for traders, affecting market liquidity and overall trading outcomes. Factors such as supply and demand, market conditions, and order types influence bid/ask prices, making it imperative for traders to grasp these concepts to navigate the complexities of financial markets effectively. From analyzing spreads impact to exploring different market structures and trading strategies, a comprehensive understanding of bid/ask prices is vital for anyone looking to succeed in trading.
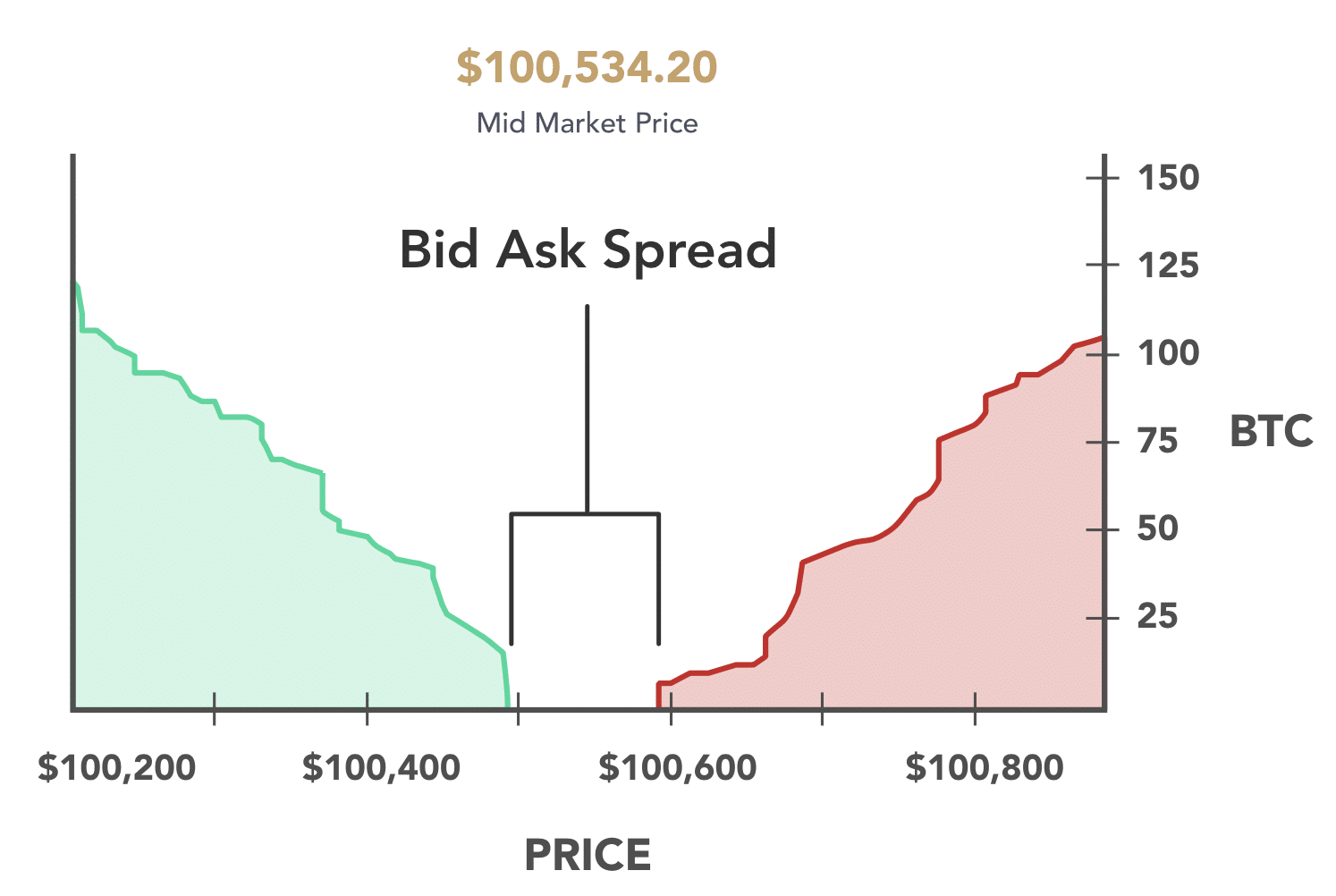
Understanding Bid/Ask Prices: A Fundamental Trading Concept
In trading, the bid price signifies the maximum amount a buyer is ready to pay for a security, indicating demand strength. Conversely, the ask price denotes the minimum price at which a seller is willing to sell, reflecting selling pressure. The spread, the variance between bid and ask prices, underpins market liquidity, offering insights into asset pricing dynamics within the market. Understanding bid/ask prices is fundamental for establishing fair value and fostering seamless trading transactions.

Understanding the Types of Bid/Ask Prices: Market, Limit, and Stop Orders
When navigating the financial markets, traders encounter different types of bid/ask prices crucial for their trading strategies. Market orders are executed instantly at the current market price, ideal for those prioritizing execution speed over price. In contrast, Limit orders allow traders to set a specific price for execution, ensuring a desired entry or exit point based on predetermined levels. Lastly, Stop orders are activated when the market hits a set price, converting into market orders to limit potential losses or lock in profits.
Market orders are attractive for traders seeking quick execution, suitable for high liquid markets or rapid price movements. Limit orders, on the other hand, grant traders more control over their entry and exit points, mitigating the risks associated with volatile market conditions. Stop orders act as a safeguard, automating trade execution based on predefined conditions, offering traders a disciplined approach to risk management and decision-making.
Depending on the trading goals and risk tolerance, each type of order serves a distinct purpose in a trader’s toolkit. Market orders are efficient for immediate trade execution, while limit orders provide price control but may risk non-execution if the market fails to reach the specified level. Stop orders act as a protective mechanism, helping traders manage risk by initiating market orders upon price movements, a valuable tool in volatile trading environments.
Incorporating a mix of market, limit, and stop orders in a trading strategy enables traders to optimize their trade execution, manage risk effectively, and capitalize on market opportunities. Understanding the nuances of each order type empowers traders to make well-informed decisions aligned with their trading objectives and risk management strategies. By strategically utilizing market, limit, and stop orders, traders can enhance their trading precision and overall performance in dynamic market conditions.
Understanding Spreads and Market Liquidity in Trading
Impact of Spread Width on Trading
Tighter spreads indicate high liquidity, facilitating swift trade execution and potentially better pricing for traders. Conversely, wider spreads can raise trading costs, leading to decreased profitability and limiting trader engagement within the market.
Influence of Liquidity on Price Discovery
Market liquidity significantly impacts price accuracy, affecting the efficiency of price discovery mechanisms. Higher liquidity enhances market transparency, aiding investors in making informed decisions based on more reliable pricing information.
The Role of Market Makers in Providing Liquidity
Market makers act as key players in maintaining liquidity by continuously quoting both bid and ask prices, narrowing spreads, and reducing trading costs. Their presence fosters a conducive trading environment, promoting market participation and efficiency.
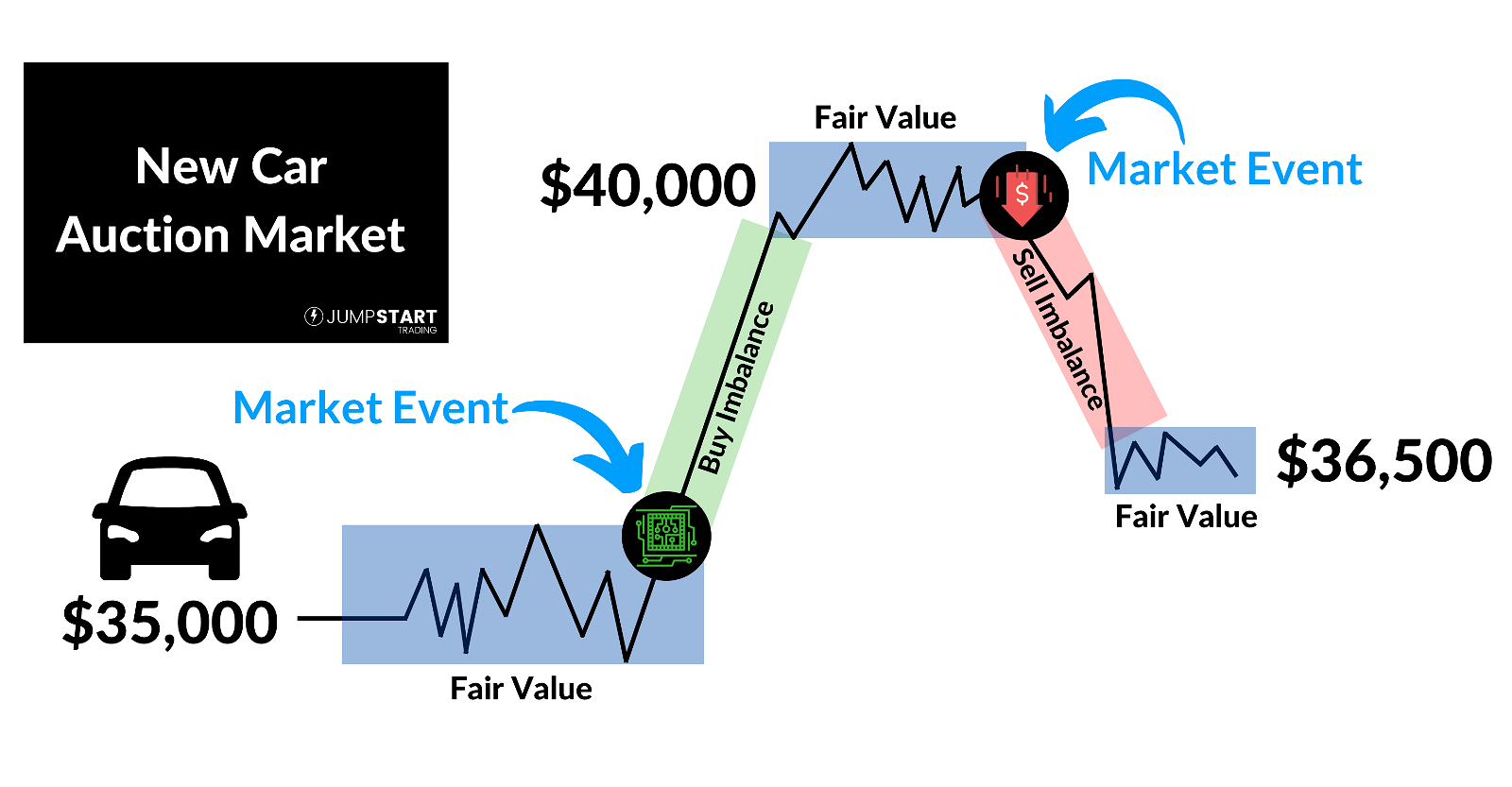
Exploring Bid/Ask Prices in Various Market Structures: Auction vs. Dealer
Understanding Auction Markets
In auction markets, bids and asks from buyers and sellers converge in a centralized platform, where prices are set through competitive bidding. This transparent process enhances price discovery and fosters fair market value for securities. Traders benefit from real-time price determination, promoting efficient trading outcomes and market integrity.
Navigating Dealer Markets
Contrastingly, dealer markets involve market makers who provide liquidity by quoting bid and ask prices. These intermediaries facilitate trades by buying and selling securities from their own inventory. The flexibility offered by dealer markets allows for quick execution of orders, contributing to market efficiency and smoother price movements.
Impact of Market Structure on Trading Strategies
The choice between auction and dealer markets significantly impacts trading strategies. Auction markets promote a more passive approach focusing on competitive pricing, whereas dealer markets encourage active trading strategies due to readily available liquidity. Understanding these structures enables traders to tailor their strategies to capitalize on market dynamics, optimizing trading performance.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Introductio_to_Technical_Analysis_Price_Patterns_Sep_2020-05-a19b59070c434400988fca7fa83898dd.jpg)
Leveraging Bid/Ask Prices for Technical Analysis
Analyzing Bid/Ask Spreads for Market Sentiment
Understanding bid/ask spreads offers valuable insights into market sentiment, showcasing the balance between buyers and sellers. Widening spreads may indicate uncertainty or increased volatility, highlighting potential price shifts. Traders keen on anticipating market movements closely monitor these spreads to make informed decisions and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Utilizing Technical Indicators for Trading Opportunities
Traders proficient in technical analysis leverage bid/ask prices alongside key indicators like support and resistance levels. By identifying price levels where the market has historically stalled or reversed, traders can pinpoint optimal entry and exit points. This strategic use of data aids in determining favorable risk-to-reward ratios in trading activities.
Identifying Breakouts and Reversals with Bid/Ask Price Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of bid/ask prices can unveil critical market dynamics, signaling potential breakout opportunities or trend reversals. Sudden shifts in bid/ask spreads or notable changes in price levels can hint at emerging market trends. By staying attuned to these fluctuations, traders position themselves to capitalize on evolving market conditions effectively.

Ethics and Best Practices in Bid/Ask Pricing: Transparency and Fairness
Market Integrity and Responsibility
Market participants bear the responsibility of providing precise and equitable bid/ask prices, fostering trust and fair trading environments. By quoting accurate prices, traders uphold market integrity and promote transparency, enhancing overall market efficiency and investor confidence.
Preventing Market Manipulation
Manipulation of bid/ask prices undermines market integrity, distorts price discovery, and poses risks to investors. Unethical practices like spoofing or layering can artificially influence prices, leading to unfair advantages and potential losses for unsuspecting market participants.
Regulatory Oversight for Fairness
Regulatory bodies play a pivotal role in monitoring trading activities to safeguard market fairness. By enforcing rules and regulations, they aim to deter misconduct, prevent manipulative behaviors, and ensure that bid/ask prices reflect true market dynamics, protecting the interests of all stakeholders.