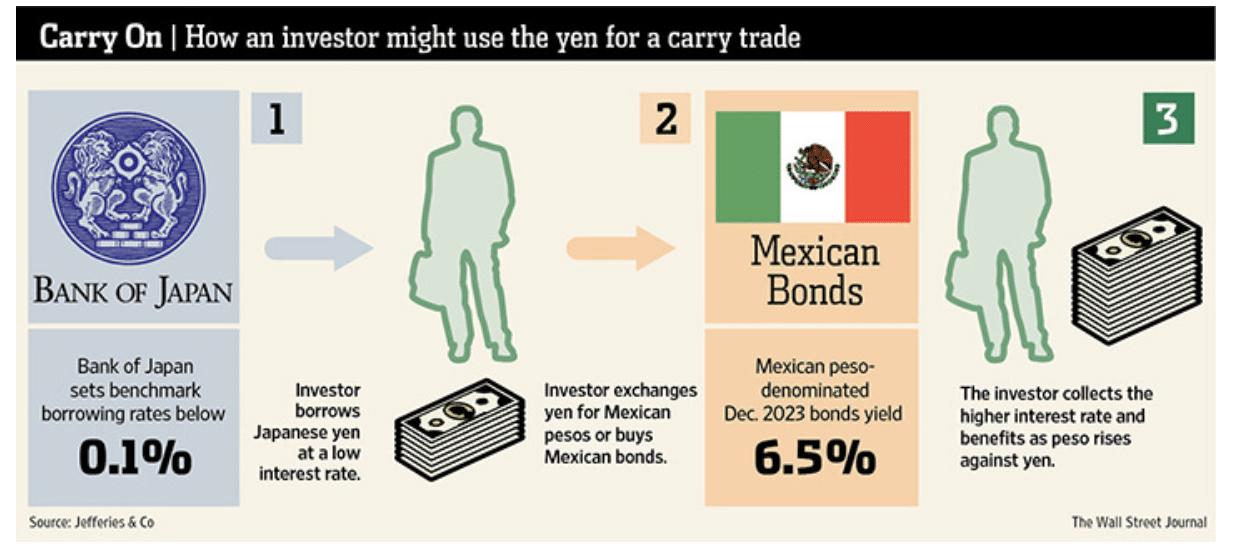
Understanding Carry Trade Strategy: A High-Risk, High-Reward Approach. Carry trade is a popular forex trading strategy that involves borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency and investing in a high-interest-rate currency to profit from the interest rate differential. This strategy is known for its potential for significant returns but also comes with high risks. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of carry trade, including its strategies, risks, and impact on the global economy.

Understanding Carry Trade: A High-Risk, High-Reward Strategy
Carry trade strategy essentially entails borrowing capital in a currency with lower interest rates and leveraging that capital into a currency offering higher interest rates, profiting from the interest rate differentials. The allure of carry trade lies in the potential for substantial gains stemming from the variance between the interest income received and the interest expenses incurred. Nonetheless, this strategy is not devoid of substantial risks, mainly stemming from the unpredictability of currency valuations and interest rate adjustments. As a result, meticulous evaluation of the risk-reward equilibrium is imperative before embarking on carry trade ventures.

Types of Carry Trade Strategies
Classic Carry Trade
Classic Carry Trade involves borrowing funds in a low-interest-rate currency, like the Japanese Yen, and investing in higher-yielding currencies, such as the New Zealand Dollar. This strategy relies on interest rate differentials to generate returns and is a fundamental approach in the carry trade strategy.
Cross-Currency Carry Trade
In Cross-Currency Carry Trade, traders borrow in one currency, for instance, the US Dollar, and diversify their investments across a basket of currencies with higher interest rates, spreading risk and potential returns across multiple assets.
Yield Curve Carry Trade
Yield Curve Carry Trade capitalizes on the yield curve’s slope. Traders borrow short-term at lower rates and invest long-term at higher rates within the same currency to profit from the yield differential over time, based on the interest rate curve’s shape.
Volatility Carry Trade
Volatility Carry Trade is based on exploiting the variance in implied volatility between currency pairs. Traders aim to profit from the difference in market expectations regarding future exchange rate fluctuations, leveraging volatility for potential gains in their trades.

Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Carry Trade Strategy entails inherent risks that traders must navigate to safeguard their investments. Currency risk is a major concern due to volatile exchange rates, potentially eroding profits. Interest rate risk poses challenges as fluctuating rates can diminish expected returns. Liquidity risk looms, affecting the ability to exit trades swiftly when market conditions turn adverse. Mitigation tactics such as hedging, diversification, and meticulous risk management are vital to counter these risks effectively.

Exploring Carry Trade in Practice: Real Stories and Valuable Insights
Historical Triumph of Japanese Yen Carry Trade
The Japanese Yen Carry Trade represents a classic example where investors borrowed in Yen at ultra-low interest rates and reinvested in high-yield currencies, reaping substantial profits. This strategy thrived in the early 2000s, demonstrating the allure of interest rate differentials for savvy traders leveraging the carry trade strategy.
Unveiling Case Studies: Profits and Losses
Various investors have navigated the unpredictable waters of carry trades, experiencing both remarkable gains and devastating losses. Analyzing these case studies sheds light on the importance of thorough risk assessment, market analysis, and a prudent approach to leveraging the carry trade strategy effectively.
Learning from Challenges: Risk Mitigation Strategies
The past is a treasure trove of valuable lessons for carry traders. By examining historical events where carry trades failed, investors can glean insights into risk management techniques, the significance of diversification, and the critical role of staying informed about global economic trends to mitigate potential losses.
Implementing Carry Trade Strategically: Adaptability in Market Dynamics
Real-world scenarios underscore the adaptability of carry trade strategies in diverse market conditions. From stable economic environments to periods of volatility, successful implementation of carry trades emphasizes the importance of flexibility, thorough research, and a keen understanding of interest rate differentials to capitalize on profitable opportunities.

Carry Trade and the Global Economy
Impact on Currency Markets and Global Liquidity
The carry trade strategy significantly impacts currency markets by influencing exchange rates based on interest rate differentials. This practice can lead to fluctuations in currency values and affect global liquidity as large volumes of funds move between currencies seeking higher returns.
Regulation by Central Banks
Central banks play a crucial role in overseeing and regulating carry trade activities to maintain stability in financial markets. They monitor the flow of capital, interest rate differentials, and intervene when necessary to prevent excessive speculation that could disrupt the global economy.
Systemic Risks and Mitigation
Excessive carry trade poses systemic risks, such as market imbalances and sudden capital outflows. Mitigation strategies include setting limits on leverage, promoting transparency, and implementing macroprudential policies to safeguard against potential financial crises triggered by carry trade activities.
Effects on Economic Growth and Inflation
Carry trade can impact economic growth by influencing capital flows and investment decisions. Increased speculative activities from carry trades can lead to asset bubbles and inflationary pressures, affecting overall economic stability and sustainability in the long run.

Exploring Alternatives to Carry Trade Strategy
Fixed Income Arbitrage
Fixed Income Arbitrage presents an alternative by capitalizing on interest rate differentials among comparable bonds. This strategy involves exploiting discrepancies in bond pricing to generate profits. By leveraging these variations, investors can potentially benefit from more stable returns compared to the volatility associated with traditional carry trade strategies.
Currency Options Trading
Currency Options Trading offers traders the flexibility to speculate on currency movements without needing to directly engage in the carry trade. By utilizing options contracts, investors can mitigate risks while still capitalizing on potential currency fluctuations. This approach provides a strategic alternative for those seeking exposure to forex markets with controlled risk.
Interest Rate Swaps
Interest Rate Swaps enable market participants to exchange cash flows based on varying interest rates, offering a way to manage interest rate exposure effectively. By entering into agreements to swap payments, investors can hedge against interest rate risks and optimize their portfolios. This alternative avenue diversifies risk and enhances risk management strategies beyond traditional carry trade approaches.
Commodities Carry Trade
Commodities Carry Trade involves investing in commodities that offer higher carry returns compared to traditional currency pairs. By exploring commodities with attractive interest differentials, traders can diversify their portfolios and potentially benefit from alternative sources of yield. This strategy allows investors to tap into commodity markets and leverage carry returns in a distinct asset class.