Understanding Fundamental Analysis: A Key to Informed Investment Decisions
Are you looking to enhance your investment decision-making skills? One essential tool to consider is fundamental analysis. Fundamental analysis provides investors with a comprehensive framework to evaluate a company’s intrinsic value through financial metrics, industry analysis, and management scrutiny. By understanding the key factors and limitations of fundamental analysis, you can make more informed investment decisions that align with your financial goals.
Delving into Fundamental Analysis for Informed Investment Decisions
Fundamental analysis, a cornerstone of smart investing, delves deep into a company’s essence by scrutinizing financial statements, industry dynamics, and leadership competence. This method seeks to uncover hidden gems or overpriced stocks, unearthing prospects for sustained growth. By dissecting fundamental parameters, investors equip themselves with the knowledge needed to navigate markets wisely, potentially reducing uncertainties. This analytical approach acts as a powerful ally to technical analysis, offering a holistic perspective beyond market sentiments and price behaviors.
Industry Analysis for Fundamental Evaluation
In the realm of Fundamental Analysis Investment Decisions, industry analysis plays a pivotal role. Understanding the industry growth rate provides insight into revenue potential, aiding investors in predicting future earnings. Delving into the competitive landscape unveils valuable information on competitors’ strategies, market positioning, and potential risks. Evaluating technological advancements helps anticipate industry shifts and opportunities, crucial for informed decision-making. Additionally, scrutinizing the regulatory environment sheds light on governmental influences that could impact industry stability and growth prospects.

Unveiling the Core: Management Team Scrutiny in Fundamental Analysis
In Fundamental Analysis Investment Decisions, scrutinizing the management team is paramount. Evaluating their experience, track record, and leadership style provides insights into their ability to drive the company’s success. Understanding their alignment of interests through ownership stake and compensation structure can gauge their commitment to shareholders. Furthermore, assessing the team’s industry knowledge reveals their strategic positioning within the competitive landscape. This thorough examination of the management team enhances decision-making accuracy in fundamental analysis.

Exploring Qualitative Factors in Fundamental Analysis
When delving into fundamental analysis for investment decisions, examining qualitative factors plays a pivotal role in assessing a company’s intrinsic value and growth potential. Let’s unravel the significance of key qualitative factors that investors should consider:
Brand Strength:
In fundamental analysis, evaluating a company’s brand strength involves assessing its brand recognition, reputation among consumers, and the level of customer loyalty it commands. Strong brand equity can translate into higher profitability and sustained market presence, influencing long-term investment decisions.
Market Share:
Understanding a company’s market share within its industry is crucial for predicting its growth trajectory. Analyzing market share provides insights into the company’s competitive position, market dominance, and potential for expanding its market presence, which are essential considerations for fundamental analysis investment decisions.
Competitive Advantages:
Identifying and understanding a company’s competitive advantages are fundamental in assessing its long-term sustainability and growth potential. These advantages may include unique products, proprietary technologies, cost efficiencies, or strong brand presence, which create barriers to entry and give the company a competitive edge in the market.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors:
Incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into fundamental analysis has gained traction among investors focused on sustainable and ethical investing. Evaluating a company’s commitment to ESG principles provides insights into its risk management practices, corporate responsibility, and long-term viability, aligning investment decisions with values and sustainability goals.
By comprehensively evaluating these qualitative factors in fundamental analysis, investors can gain a holistic understanding of a company’s potential for growth, resilience in competitive environments, and alignment with sustainable investing practices, guiding well-informed investment decisions.
Limitations and Challenges of Fundamental Analysis
When delving into the world of Fundamental Analysis Investment Decisions, one must acknowledge the inherent subjectivity in interpreting financial data and industry trends. Differing analyst perspectives can lead to varied conclusions, influencing investment decisions.
The challenge of future uncertainty looms large over fundamental analysis. Despite its thorough evaluation of historical data, fundamental analysis falls short in predicting unforeseen events or sudden market fluctuations, leaving investors vulnerable to unexpected outcomes.
A significant drawback of fundamental analysis is its time-consuming nature. Conducting a comprehensive analysis demands a substantial allocation of time and resources, making it impractical for quick decision-making processes or reacting promptly to market changes.
Fundamental analysis, while robust in evaluating long-term investment opportunities, may not be well-suited for highly speculative or short-term investment strategies. Its emphasis on intrinsic value and company fundamentals can limit its effectiveness in rapidly changing or volatile markets.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FundamentalAnalysis_Final_4195918-eea2436ba2374e23930b0a482adbea2f.jpg)
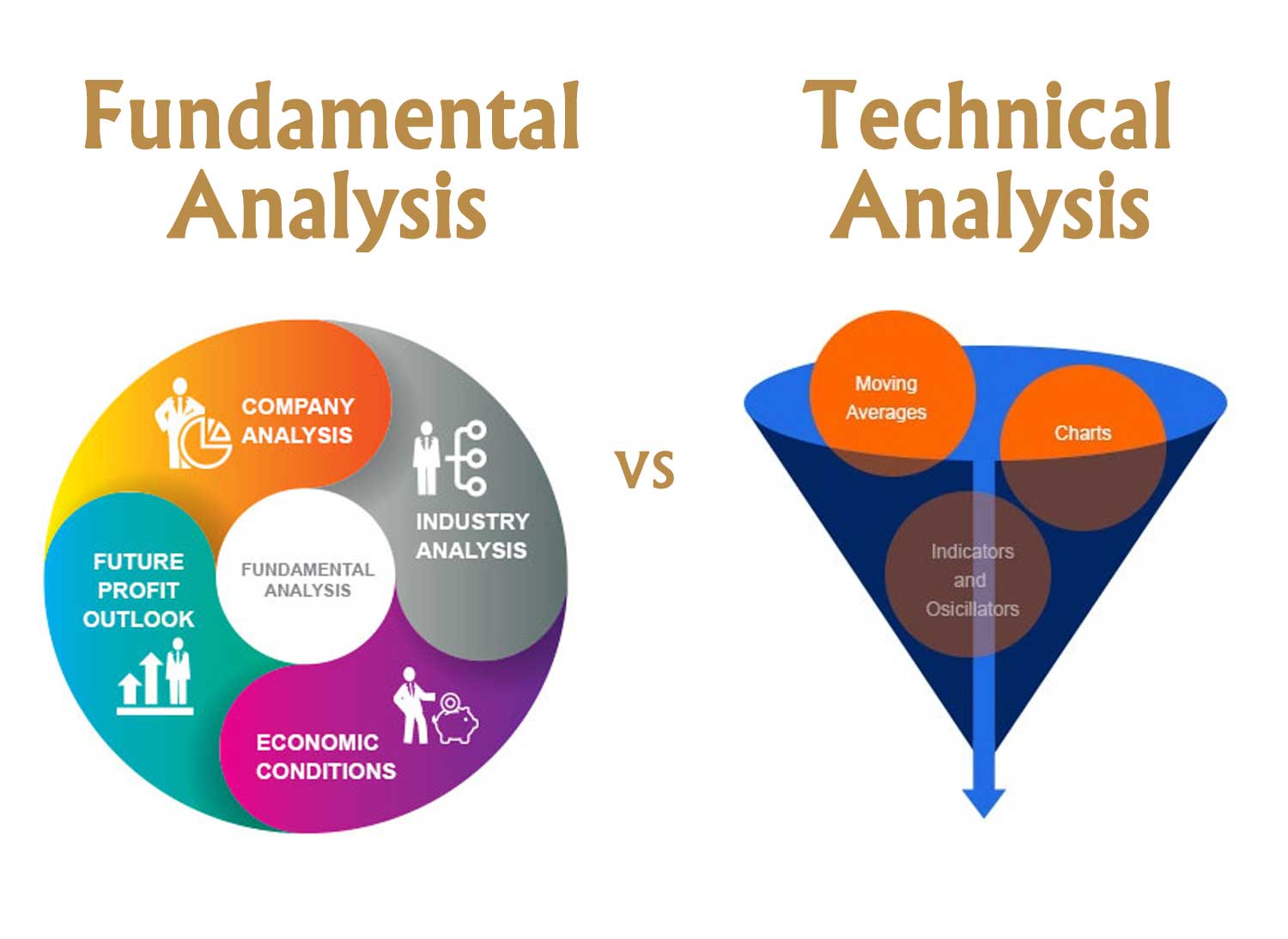
Integrating Fundamental and Technical Analysis: A Holistic Approach to Informed Investment Decisions
By amalgamating fundamental and technical analysis, investors gain a thorough perspective on a company’s potential and risks. While technical analysis shines in pinpointing short-term trade chances, fundamental analysis is the compass for enduring investment moves. The synergy of both methods empowers investors to navigate the markets wisely, fostering well-rounded and knowledgeable investment selections. Notably, fundamental analysis predominantly caters to the needs of long-term investment strategies.