Understanding inflation is crucial for individuals and policymakers alike to navigate the complexities of the economy. Inflation, the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, impacts everything from consumer purchasing power to interest rates and investment decisions. In this article, we will delve into the causes behind inflation, its far-reaching impacts on society and the economy, and the effective strategies for tackling and managing it. Let’s explore the multifaceted nature of inflation and how it shapes the financial landscape globally.
Inflation, a persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, can have profound effects on various aspects of our lives. From influencing consumer behavior and savings to shaping government policies and business operations, inflation permeates every corner of the economy. This article aims to dissect the intricate mechanisms driving inflation, analyze its implications on different sectors, and present actionable strategies for mitigating its adverse effects. Join us on a journey to grasp the intricacies of inflation and discover proactive measures to safeguard economic stability and growth.

Unveiling the Dynamics of Inflation: A Comprehensive Insight
Inflation, a persistent rise in the overall price levels of goods and services over time, serves as a crucial economic indicator. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI) are fundamental metrics used to quantify inflation’s magnitude and impact. Understanding inflation causes and impacts delves into a realm where demand fluctuations, supply disruptions, and monetary policy intricacies intertwine to shape economic landscapes. Moderate inflation can signify economic vigor, fostering growth, while excessive levels can instigate economic instabilities, undermining consumer purchasing power and economic equilibrium.
![]()
Exploring the Causes and Consequences of Inflation
Unraveling the Forces Behind Inflation
Understanding inflation causes and impacts is vital in economic analysis. Demand-pull inflation arises from heightened consumer demand, inducing price hikes. Conversely, cost-push inflation stems from supply constraints, escalating production expenses and subsequently prices. Balancing these dynamics is key in curbing inflationary pressures.
Navigating the Implications of Soaring Inflation
When inflation surges, citizens grapple with diminished purchasing power, hampered savings, and sluggish economic expansion. Moreover, prolonged high inflation rates can stir social discontent, straining societal harmony and stability. Vigilance and adept policy responses are crucial to mitigate the adverse fallout of escalating inflation.
The Specter of Hyperinflation: A Looming Catastrophe
Hyperinflation, the nightmare scenario of uncontrollable price spirals, heralds economic turmoil and currency devaluation. This extreme form of inflation erodes trust in financial systems, triggering chaos and economic paralysis. Safeguarding against hyperinflation demands prudent economic management and steadfast policy interventions to avert catastrophic consequences.
By dissecting the roots and repercussions of inflation with a focus on its causes and consequences, stakeholders can navigate economic complexities adeptly. Grasping these intricacies empowers individuals, policymakers, and investors to make informed decisions, fortifying economic resilience and sustainability in the face of inflationary pressures.
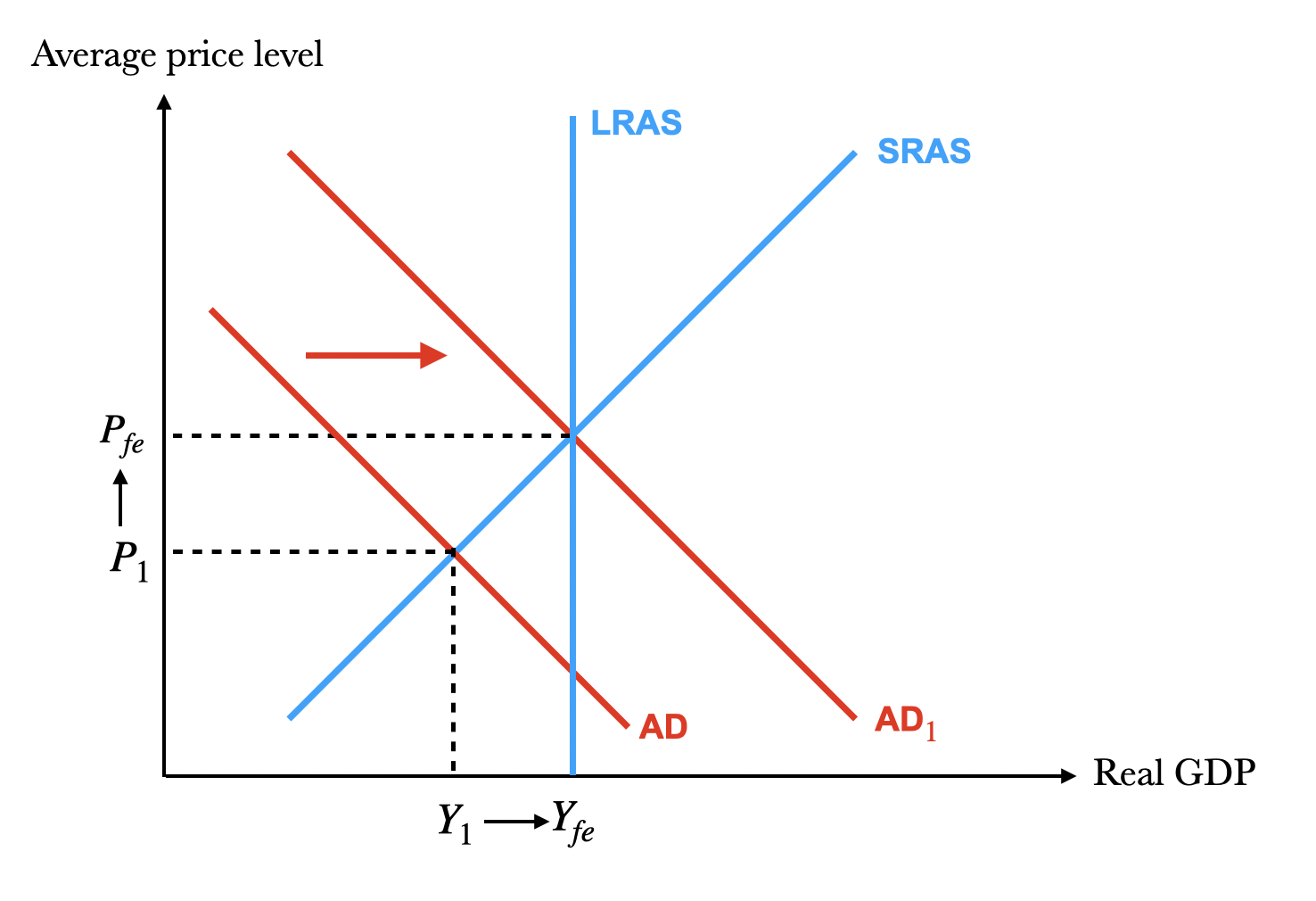
The Role of Fiscal Policy in Managing Inflation
Fiscal policy, encompassing government spending and taxation decisions, plays a significant role in influencing inflation dynamics. When governments implement expansionary fiscal policies like boosting spending or reducing taxes, it can spur consumer demand, potentially fueling inflationary pressures as more money chases fewer goods and services. Conversely, contractionary fiscal measures, like cutting spending or raising taxes, can act as a brake on inflation by dampening aggregate demand.
Governments face a delicate balancing act when crafting fiscal policies, especially concerning inflation management. Striking the right equilibrium between stimulating the economy through fiscal measures and preventing runaway inflation requires astute policymaking. By monitoring economic indicators, policymakers can gauge the optimal mix of fiscal interventions to foster growth while keeping inflation in check. Careful consideration of these trade-offs is crucial for achieving macroeconomic stability and sustainable growth.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate relationship between fiscal policy and inflation is essential for policymakers to navigate economic challenges effectively. By employing suitable fiscal measures in response to inflationary pressures, governments can wield a powerful tool in balancing economic expansion with price stability. A nuanced approach to fiscal policy formulation is critical in promoting a healthy economic environment where inflation remains under control, laying the foundations for robust and sustainable growth.
Exploring Inflation and Investment Strategies
Investors must grasp how inflation influences their investments. Inflation’s corrosive effect on fixed-income assets like bonds can diminish their real returns over time. While equities and real estate can offer a hedge against inflation, market fluctuations can affect their efficacy in preserving value. Optimal diversification and strategic asset allocation play pivotal roles in mitigating inflation’s impact on investment portfolios, enhancing resilience in volatile economic climates.
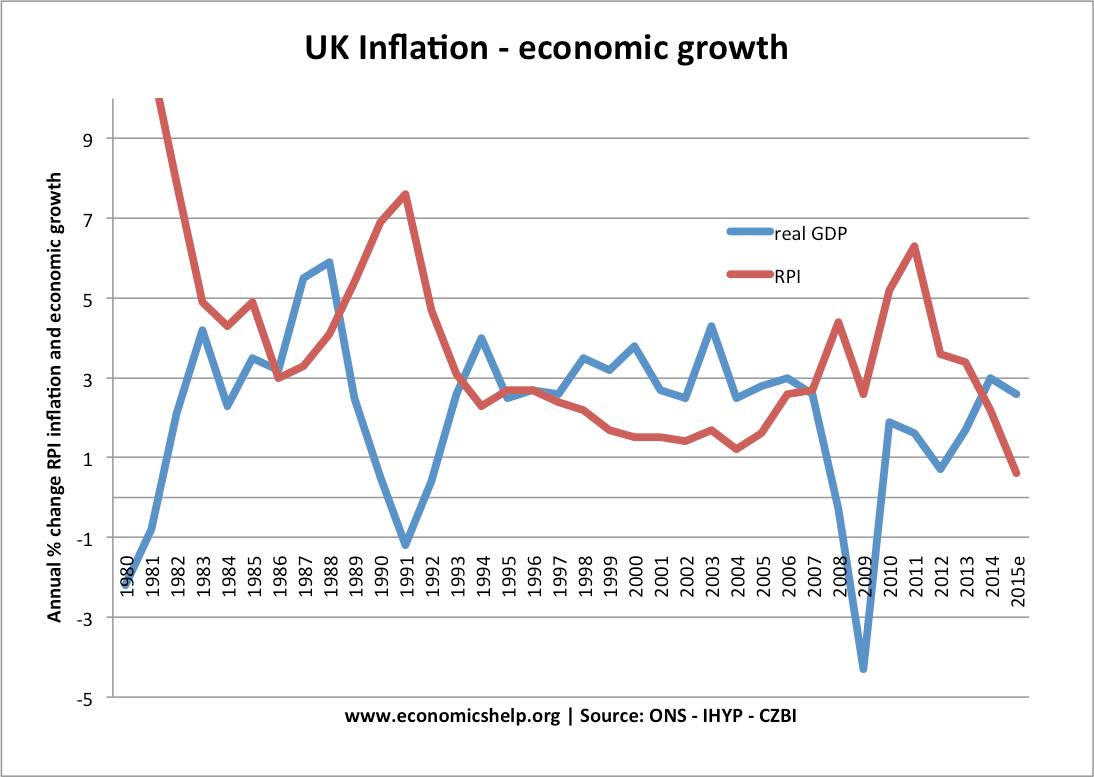
Balancing Inflation and Economic Growth
Impact of Inflation on Economic Growth
Moderate inflation often signals a healthy, expanding economy, reflecting rising consumer demand and economic activity. This level of inflation can encourage spending and investment, stimulating growth and job creation within an economy.
Risks of High Inflation
Conversely, high inflation poses risks to economic growth by eroding purchasing power, diminishing consumer confidence, and discouraging long-term investments. It can lead to uncertainty, reduced consumer spending, and volatility in financial markets, hindering economic progress.
The Role of Governments and Central Banks
Governments and central banks play a vital role in maintaining a delicate balance between curbing excessive inflation and fostering sustainable economic growth. Effective monetary and fiscal policies are essential tools in managing inflation while supporting overall economic expansion.
Implementing Structural Reforms
To combat inflation without impeding growth, structural reforms like enhancing productivity and implementing supply-side policies are crucial. These reforms aim to address underlying economic inefficiencies, boost competitiveness, and create a more stable environment conducive to both controlled inflation and sustainable growth.
By understanding the intricate relationship between inflation and economic growth, policymakers and stakeholders can implement informed strategies to ensure a harmonious balance that promotes economic prosperity while mitigating inflationary pressures. Through proactive measures and a comprehensive approach to policy-making, economies can navigate the complexities of inflation dynamics to achieve long-term stability and growth.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-hyperinflation-definition-causes-and-examples-3306097-Final-58ea47ee1dd94b16b061214dcc8dae77.png)
The Social Dynamics of Inflation: Understanding the Impact
Inflation fundamentally alters the financial landscape, profoundly impacting individuals and society at large. High inflation particularly burdens low-income households and those with fixed incomes, exacerbating financial disparities. Moreover, the devaluation of savings and retirement funds undercuts financial security, necessitating proactive measures.
Inflation’s Unequal Toll on Society
Understanding Inflation Causes and Impacts illuminates how inflation’s effects are not uniform. Vulnerable groups, like low-income individuals and retirees, bear the brunt of escalating prices, facing diminished purchasing power and economic insecurity. Mitigating these disparities demands targeted interventions and equitable policies.
Safeguarding Finances Against Inflation’s Erosion
The erosion of savings and retirement funds due to inflation poses a significant challenge. It underscores the importance of long-term financial planning and diversified investments to weather inflationary pressures effectively. Governments play a vital role in creating mechanisms to shield citizens from inflation’s detrimental effects.
Policy Imperatives for Social Protection
Governments play a crucial role in safeguarding vulnerable populations from the adverse consequences of inflation. Implementing targeted policies, such as social welfare programs and cost-of-living adjustments, is imperative to mitigate the socio-economic impacts of inflation. Ensuring equitable access to resources is essential for fostering financial stability and social well-being.
By delving into the intricate relationship between inflation and social impact, we unravel the complexities of economic disparities and the urgency of implementing inclusive policies to safeguard the most vulnerable members of society. prioritizing social welfare can build resilience and promote equitable economic development for a more sustainable future.