In the realm of global banking and finance, the Bank of Japan stands as a key player with a multitude of responsibilities and a rich historical background. As a pivotal institution in shaping Japan’s economic landscape, the Bank of Japan plays a crucial role in implementing monetary policies, regulating financial activities, and influencing the country’s inflation rates. Understanding the Bank of Japan’s mandate and operations is essential for grasping the intricacies of Japan’s financial system and its impact on the international market.
With a deep dive into the Bank of Japan’s functions and policies, this comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the institution’s mechanisms for monetary control, its strategies for inflation targeting, and its evolving role in the global financial arena. From its historical evolution to its current challenges and future prospects, this article will explore how the Bank of Japan navigates through economic uncertainties and contributes to Japan’s economic stability, all while addressing the complexities of financial regulation and international collaborations.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Monetary-Policy-ca2313abbf3646e38301b40f3a53a476.png)
Unveiling the Bank of Japan’s Vital Role and Mandate
The Bank of Japan, as Japan’s central bank, holds the critical responsibility of steering the nation’s monetary policy and overseeing its financial system. At its core, the Bank of Japan’s primary mandate revolves around upholding price stability and fostering sustainable economic growth within the country.
Diving into its operational toolkit, the Bank of Japan wields a diverse array of instruments to impact the economy significantly. From finely tuning interest rates to implementing large-scale asset purchases through quantitative easing, the Bank can steer economic trajectories with precision.
Beyond monetary policy, the Bank of Japan stands tall in the realm of financial regulation, safeguarding the integrity and robustness of Japan’s banking sector. By acting as a guardian of financial stability, the Bank plays a pivotal role in maintaining the soundness of the country’s financial institutions.

Evolution of the Bank of Japan: Shaping Japan’s Financial Landscape
The inception of the Bank of Japan in 1882, mirroring European central banks, marked a pivotal moment in Japan’s financial history. Over time, the bank experienced transformative reforms, notably post-WWII and in the 1990s. These changes sculpted the institution’s structure, functions, and policy arsenal, reflecting its adaptability to economic shifts.
During each reform wave, the Bank of Japan redefined its mandates and tools, aligning them with contemporary economic challenges. These adaptations allowed the bank to actively contribute to Japan’s economic progress and maintain financial equilibrium during turbulent periods, showcasing its pivotal role in steering the country’s monetary landscape towards stability.
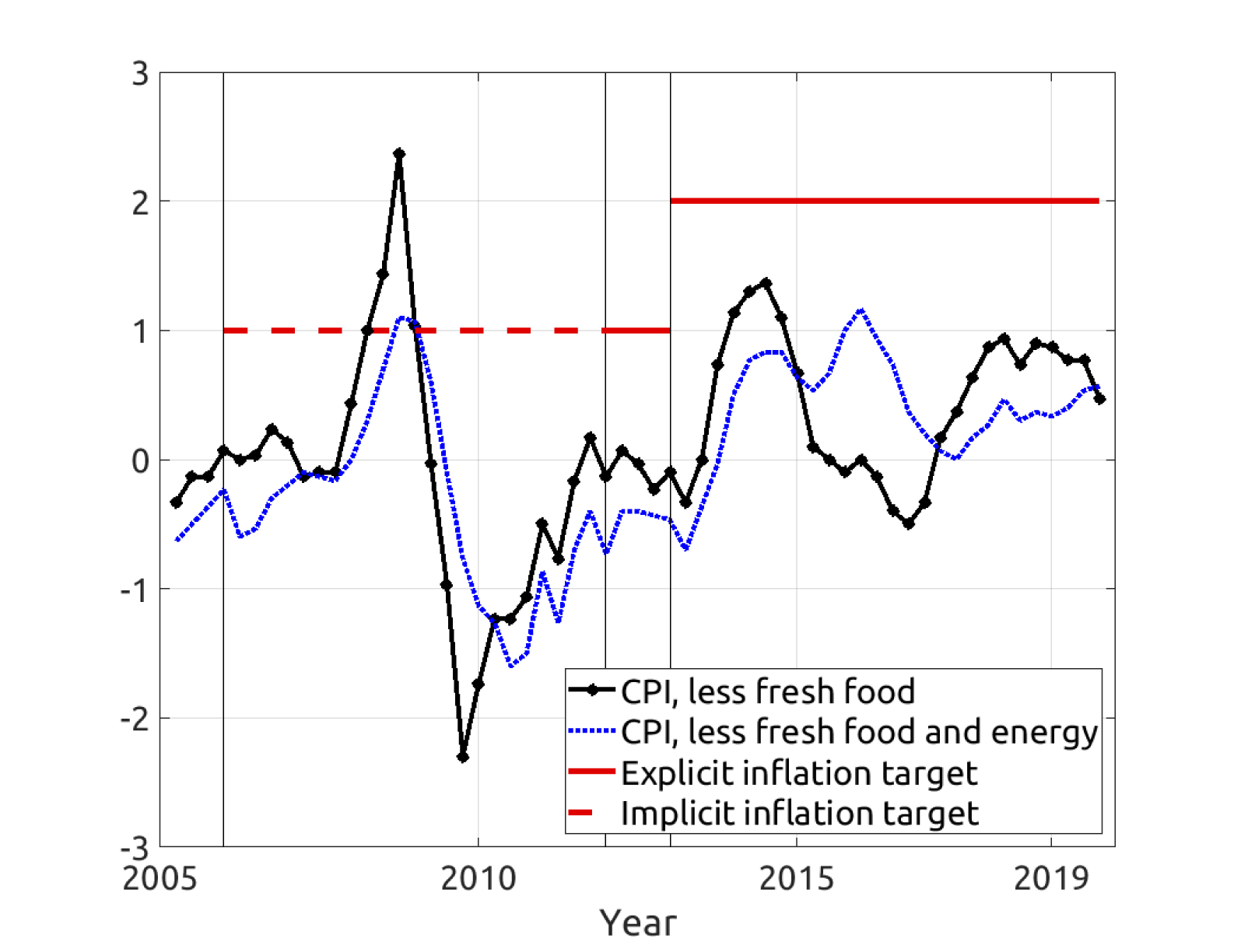
The Bank of Japan and Inflation Targeting
The Bank of Japan solidified its commitment to economic stability by embracing an inflation targeting strategy in 2013. Setting a 2% inflation target aimed to combat deflation and stimulate sustainable economic growth. Despite concerted efforts, achieving this goal proved challenging amidst persistent deflationary forces and subdued economic expansion. Consequently, the Bank of Japan persists in deploying accommodative monetary policies to invigorate inflationary trends.

The Bank of Japan’s Role in Financial Regulation
The Bank of Japan plays a pivotal role in regulating banks and other financial institutions in Japan, overseeing their functions for stability. Through prudential regulations, the Bank ensures the financial system’s safety and soundness, safeguarding against risks. By conducting stress tests and monitoring systemic vulnerabilities, it actively works to maintain financial stability and protect the interests of depositors.

Challenges and Prospects for the Bank of Japan
The Bank of Japan role and mandate encounters hurdles like persistently low inflation, an aging demographic landscape, and unpredictable global economic shifts. Striking a delicate equilibrium between ensuring price stability and fostering economic advancement poses a significant challenge for the institution. To combat these obstacles, the Bank of Japan is actively exploring innovative policy instruments and strategies to navigate through the evolving economic terrain.
As the financial landscape continues to shift, the future trajectory of the Bank of Japan hinges on its capacity to adeptly respond to fluctuating economic dynamics while upholding financial stability. Embracing flexibility and agility in its operations will be pivotal for the institution’s sustained relevance and effectiveness in preserving Japan’s economic health amidst a backdrop of uncertainties and changing market demands.
